In our fast-paced world, sleep often takes a back seat to other priorities. Yet, maintaining a regular sleep schedule is crucial for overall health and well-being.
A poor sleep pattern can have a multitude of adverse effects on mental health, physical health, cognitive function, and overall quality of life. Understanding these impacts and how to improve sleep habits is essential for anyone looking to lead a healthier life.
The Mental Health Connection
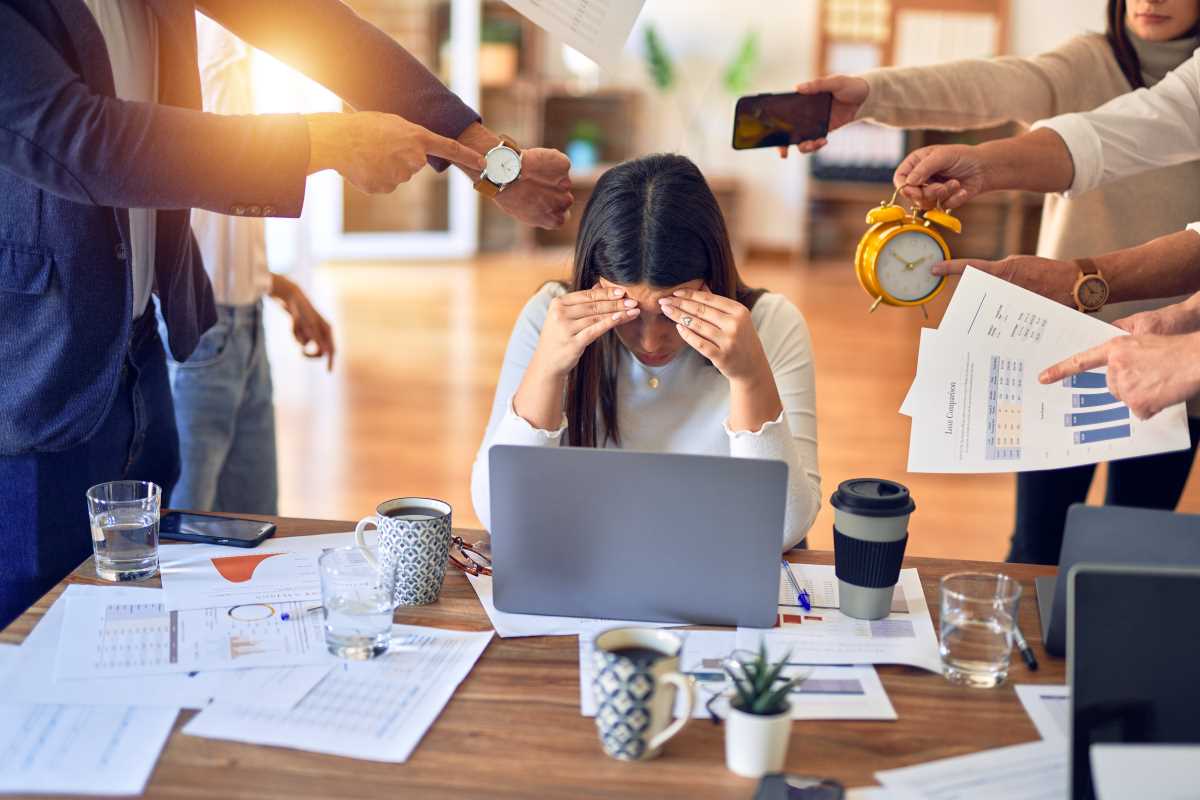
One of the most immediate effects of a bad sleep schedule is its impact on mental health. Sleep is essential for emotional regulation and mental resilience. Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress, anxiety, and depression.
When you don’t get enough rest, the brain's ability to manage stress hormones decreases, leading to heightened stress levels. This can create a vicious cycle where stress causes poor sleep, and poor sleep increases stress.
Moreover, insufficient sleep can affect mood and emotional responses. It becomes harder to manage emotions, leading to irritability and mood swings.
Over time, chronic sleep deprivation can contribute to the development of mood disorders. Prioritizing sleep is, therefore, not just about feeling rested; it’s about maintaining mental health stability.
Physical Health and Immune Function
The body undergoes critical repair processes during sleep, affecting everything from muscle recovery to immune function.
A disrupted sleep schedule can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to illnesses. This means you're more likely to catch colds or other infections due to reduced defense mechanisms.
Furthermore, poor sleep is linked to weight gain and obesity. Sleep deprivation affects the hormones that regulate hunger, leading to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods.
- This can contribute to weight gain and associated health problems such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps balance these hormones, reducing the risk of health complications.
Impaired Cognitive Function
Sleep is vital for cognitive processes, including memory consolidation, problem-solving, and concentration. A disrupted sleep routine can severely impair cognitive function, making it difficult to focus, retain information, and perform complex tasks.
Sleep deprivation affects the brain's ability to process information efficiently, leading to slower reaction times and increased errors.
For students and professionals alike, poor sleep can hinder academic and work performance. Memory consolidation occurs during sleep, meaning that information learned during the day is better retained and understood after a good night's rest.
Ensuring adequate sleep is not just beneficial but crucial for cognitive health and productivity.
Overall Well-Being and Lifestyle
Beyond mental and physical health, a bad sleep schedule can affect overall well-being and quality of life.
- Sleep deprivation can lead to decreased energy levels, making it difficult to engage in daily activities or exercise.
- This lack of energy can impact social interactions and relationships, as fatigue often leads to withdrawal and reduced participation in social activities.
Chronic sleep issues can also detract from life satisfaction. When tired, people often lack the enthusiasm and motivation to pursue hobbies or interests, leading to a diminished sense of fulfillment.
By improving sleep habits, individuals can experience increased vitality and engagement in their daily lives.
Tips for Improving Sleep Habits
Establish a Regular Bedtime Routine: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate the body's internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally. Consistency is key, even on weekends.
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Consider blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines if necessary. Ensure your mattress and pillows provide adequate comfort and support.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: The blue light emitted by phones, tablets, and computers can interfere with the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. Try to avoid screens at least an hour before bed.
- Manage Stress: Stress and anxiety can be significant barriers to a good night's sleep. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga into your routine can help calm the mind.
- Watch What You Eat and Drink: Avoid large meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. These can disrupt sleep patterns and make it harder to stay asleep through the night.
- Get Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help you fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep. However, try to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it can have the opposite effect.
A poor sleep schedule does more than just make you feel groggy; it can have far-reaching impacts on every aspect of your health and well-being. From mental and physical health to cognitive function and lifestyle satisfaction, regular, restful sleep is essential.
By implementing practical tips to improve sleep habits, you can enhance your quality of life significantly. Remember, prioritizing sleep is an investment in your health, enabling you to live a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
 (Image via
(Image via